Image Source: images.ctfassets.net
How Do You Become An Art Teacher? Your Guide
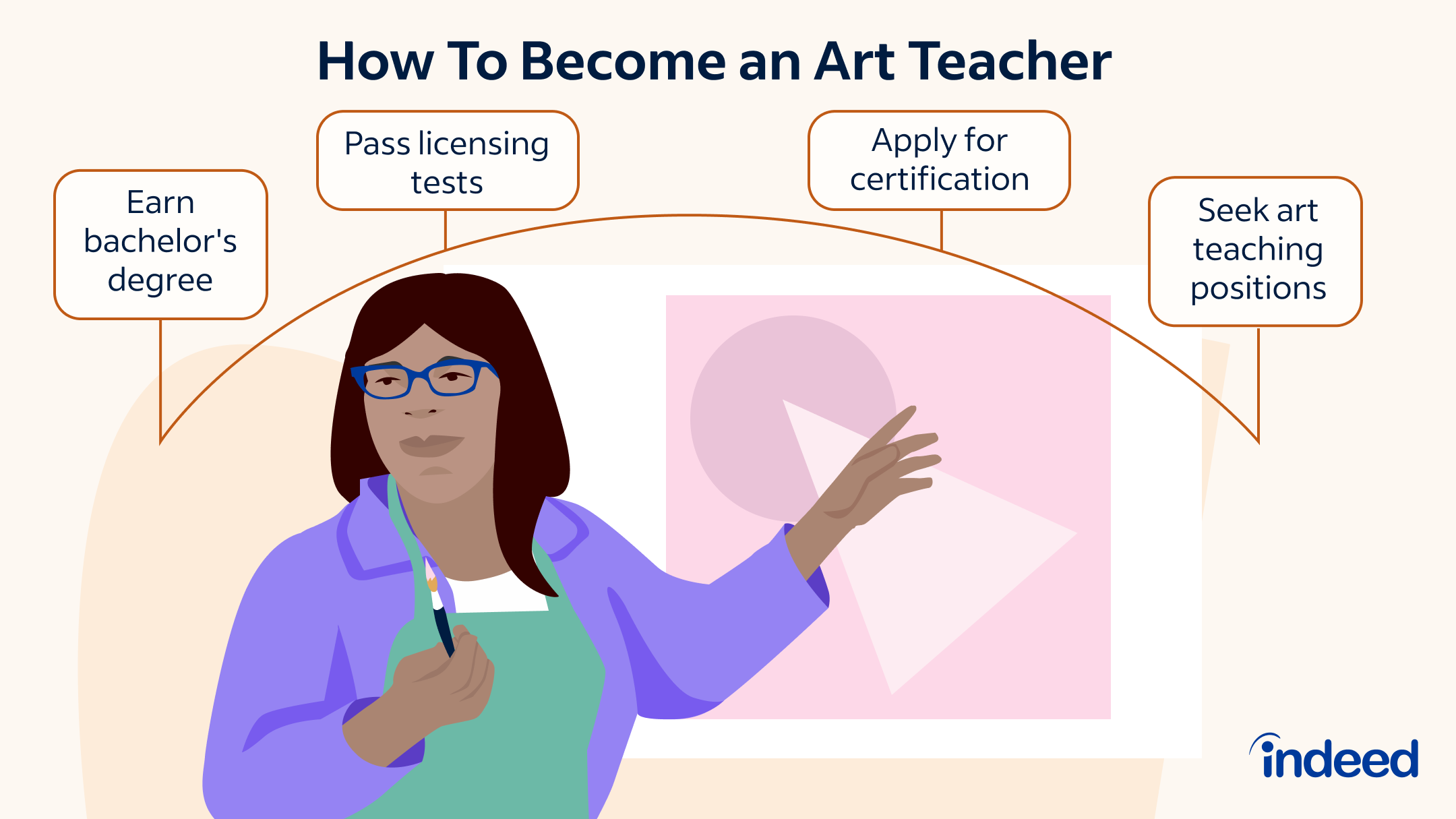
To become an art teacher, you typically need a bachelor’s degree in art or art education, followed by obtaining an art education certification or art teaching license in the state or country where you wish to teach. So, what are the steps to embark on this fulfilling career path? This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about becoming an art educator.
The journey to becoming an art teacher is a rewarding one, blending a passion for creativity with the fulfillment of nurturing young minds. Whether your dream is to guide little hands in creating their first masterpieces as an elementary art teacher or to inspire teenagers with complex artistic concepts as a secondary art teacher, the path requires dedication and specific preparation. This guide will break down the essential steps, from acquiring the necessary qualifications to developing the skills needed for successful art curriculum development and teaching art in schools.
The Foundation: Education and Qualifications
At the heart of becoming an art teacher lies a solid educational foundation. Most positions require a bachelor’s degree, and often, a specialized art teaching degree is the most direct route.
Bachelor’s Degree in Art or Art Education
Your initial step is to earn a bachelor’s degree. You generally have two main options here:
- Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA) with a concentration in Art Education: This degree typically focuses heavily on studio art practice, offering a deep dive into various artistic mediums. The art education component will cover pedagogical methods specific to teaching art.
- Bachelor of Arts (BA) in Art History or Studio Art with a minor in Education: This path allows for a broader academic study of art, with a secondary focus on educational principles. You will likely need to complete additional coursework or a post-baccalaureate program to meet teaching certification requirements.
- Bachelor of Science (BS) in Art Education: This degree is specifically designed to prepare individuals for teaching art in K-12 settings. It usually combines a strong foundation in art history and studio practice with robust pedagogical training and practical teaching experience.
When choosing a program, look for those accredited by recognized educational bodies. Accreditation ensures the program meets quality standards and that your degree will be recognized by state licensing boards.
Art Education Certification and Licensing
Once you have your degree, the next crucial step is securing your art education certification or art teaching license. The exact requirements vary significantly by state in the U.S., and by country internationally.
Common components of obtaining an art teaching license include:
- Completion of an accredited art education program: This is the degree mentioned above, designed to equip you with both artistic knowledge and teaching skills.
- Passing state-specific licensing exams: These exams often assess your knowledge of art history, studio art techniques, art pedagogy, and your ability to apply these in a classroom setting. Some states may also require general teaching competency exams.
- Background checks: A clean criminal record is usually a prerequisite for working with children.
- Student teaching or practicum experience: This is an invaluable part of your art teacher training programs. You’ll work under the guidance of experienced art teachers in real classroom environments, gaining hands-on experience in lesson planning, classroom management, and student assessment.
Key areas assessed in art education certification exams often include:
- Art History and Theory: Knowledge of major art movements, artists, and cultural contexts.
- Studio Art Practices: Proficiency in various art disciplines like drawing, painting, sculpture, printmaking, digital art, and crafts.
- Art Pedagogy: Strategies for teaching art effectively, including lesson planning, differentiated instruction, assessment techniques, and classroom management.
- Child Development: Understanding how students learn and develop at different age levels.
It’s essential to research the specific requirements of the state or region where you intend to teach early in your academic career. Websites for state departments of education are the best resource for up-to-date information on art teaching license requirements.
Developing Essential Skills for an Art Instructor Career
Beyond formal education, a successful art instructor career hinges on a robust set of skills. These are honed through your degree program, student teaching, and ongoing professional development.
Artistic Proficiency and Creativity
This might seem obvious, but a deep understanding and demonstrable skill in various art forms are paramount. This includes:
- Studio Techniques: Mastery of drawing, painting, sculpture, printmaking, digital media, and potentially other crafts. You should be comfortable demonstrating these techniques to students.
- Art History and Appreciation: A strong knowledge base allows you to contextualize student work and introduce them to diverse artistic traditions.
- Creative Problem-Solving: The ability to think outside the box, experiment with materials, and find innovative solutions to artistic challenges.
Pedagogical Skills
Effective teaching involves more than just knowing your subject matter. It requires understanding how to impart that knowledge and inspire students.
- Lesson Planning: Designing engaging, age-appropriate lessons that align with curriculum standards and learning objectives. This involves art curriculum development that is both informative and inspiring.
- Classroom Management: Creating a safe, respectful, and productive learning environment where students feel encouraged to explore and express themselves.
- Differentiated Instruction: Adapting teaching methods and materials to meet the diverse needs and learning styles of all students.
- Assessment: Evaluating student progress through various methods, including observation, critique, and portfolio reviews, to inform future instruction.
- Communication: Clearly explaining concepts, providing constructive feedback, and fostering positive relationships with students, parents, and colleagues.
Curriculum Development and Implementation
As an art teacher, you’ll be responsible for not just delivering lessons but also for shaping the art curriculum.
- Understanding Standards: Familiarizing yourself with national and state standards for art education ensures your curriculum is comprehensive and meets educational benchmarks.
- Sequencing Learning: Developing a logical progression of skills and concepts throughout a school year or across grade levels.
- Material Selection: Choosing appropriate art materials and tools that are safe, accessible, and conducive to learning.
- Integration: Finding ways to connect art with other subjects, showing students the relevance of art across disciplines.
Interpersonal Skills
The ability to connect with people is vital for any teacher.
- Patience and Empathy: Art can be challenging, and students will have different levels of confidence and skill.
- Enthusiasm: Your passion for art will be contagious and can inspire students to embrace their own creativity.
- Collaboration: Working effectively with other teachers, administrators, and parents.
Exploring Different Art Teaching Roles
The path to becoming an art teacher can lead to various educational settings, each with its unique demands and rewards.
Elementary Art Teacher Requirements
Teaching art to young children requires a focus on foundational skills, exploration, and sensory engagement.
- Degree: A Bachelor’s degree in Art Education is often preferred, or a related art degree with a strong emphasis on early childhood or elementary education.
- Certification: Elementary art teacher requirements typically include general elementary education certification, possibly with an art endorsement, or a specific K-6 art teaching license.
- Skills: Patience, creativity, adaptability, and the ability to make art fun and accessible for young learners are crucial. Understanding child development is key.
- Curriculum: Focuses on basic art elements (line, shape, color, texture), introducing diverse media, fostering imagination, and encouraging self-expression.
Secondary Art Teacher Qualifications
For middle and high school students, the focus shifts towards developing more sophisticated artistic techniques, critical thinking, and personal artistic voice.
- Degree: A Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in Art Education, or a Fine Arts degree with a concentration in a specific discipline (e.g., painting, sculpture) and a teaching certification.
- Certification: Secondary art teacher qualifications usually require a specific art teaching license for grades 7-12 or 9-12.
- Skills: Deep knowledge of art history and theory, proficiency in various artistic mediums, ability to provide constructive critique, and skills in managing larger class sizes.
- Curriculum: May include specialized courses in drawing, painting, ceramics, photography, digital art, and art history, encouraging students to develop their individual styles and explore conceptual ideas.
Other Art Teaching Settings
Beyond traditional K-12 schools, opportunities exist in:
- Community Centers and Art Studios: Offering workshops and classes to people of all ages.
- Museums: Developing educational programs and leading tours.
- Colleges and Universities: Requiring advanced degrees (Master’s or PhD) and often significant professional experience.
- Online Platforms: Creating and delivering art lessons virtually.
The Art Teacher Training Programs Landscape
Art teacher training programs are designed to equip aspiring educators with the necessary knowledge and skills. These programs are typically found within university education departments.
Key components of quality art teacher training programs:
- Studio Art Courses: Building a strong foundation in visual arts.
- Art History and Criticism: Providing historical and theoretical context.
- Pedagogy and Curriculum: Teaching the science and art of teaching.
- Psychology of Learning: Understanding how students learn.
- Practicum and Student Teaching: Gaining real-world experience in diverse school settings.
- Technology in the Art Classroom: Integrating digital tools and resources.
When researching programs, consider their accreditation, faculty expertise, available resources, and the success rate of their graduates in obtaining art teaching licenses and employment.
Navigating the Job Market and Professional Development
Once you have your qualifications, the next step is to secure a position and continue growing as an educator.
Crafting Your Resume and Portfolio
Your resume should highlight your educational background, teaching experience, artistic skills, and any relevant volunteer work. Your art portfolio is equally, if not more, important. It should showcase your best artwork, demonstrating your technical ability and creative vision. For teaching positions, it’s also beneficial to include examples of student work that demonstrate your teaching effectiveness.
The Interview Process
Be prepared to discuss your teaching philosophy, classroom management strategies, and how you approach art curriculum development. You may also be asked to present a sample lesson plan or demonstrate a specific art technique.
Continuous Professional Development
The field of education is always evolving. To remain an effective art instructor, engage in continuous learning:
- Attend Workshops and Conferences: Stay updated on new teaching methodologies, technologies, and artistic trends.
- Join Professional Organizations: Connect with other art educators, share ideas, and access resources. Examples include the National Art Education Association (NAEA) in the U.S.
- Pursue Advanced Degrees: A Master’s or Doctoral degree can open doors to leadership roles and specialized teaching positions.
- Stay Creative: Continue to create your own art. This keeps your skills sharp and your passion alive.
Frequently Asked Questions About Becoming an Art Teacher
Q1: Can I become an art teacher with a degree in a different subject?
Yes, it is often possible, but you will likely need to complete additional coursework in art and education, and potentially a post-baccalaureate certification program, to meet the specific requirements for an art teaching license.
Q2: What is the difference between an art education certification and an art teaching license?
While often used interchangeably, a certification is typically an endorsement granted by an institution after completing a specific program. A license is the official permit issued by a state or governing body that allows you to teach in public schools. The requirements for a license are usually more rigorous and legally binding.
Q3: How long does it take to become an art teacher?
Typically, a bachelor’s degree takes four years. If this degree is in Art Education and includes your student teaching, you can often be eligible for initial certification upon graduation. Additional certifications or advanced degrees will extend this timeline.
Q4: What are the most important qualities of an art teacher?
Key qualities include creativity, patience, strong communication skills, passion for art and teaching, adaptability, a solid understanding of art principles and history, and excellent classroom management skills.
Q5: Is it difficult to find a job as an art teacher?
Job availability can vary by region and school district. Having strong qualifications, relevant experience, and a compelling portfolio can significantly improve your chances. Networking within the education community is also beneficial.
Q6: Do I need to be a professional artist to teach art?
While being a skilled artist is important, a professional career as a practicing artist is not always a strict requirement for teaching art in schools. However, a strong artistic portfolio and ongoing engagement with your own creative practice are highly valued. The ability to effectively translate your artistic knowledge and passion into a teachable format is paramount.
Q7: What is the role of art curriculum development in teaching art in schools?
Art curriculum development is fundamental. It ensures that students receive a well-rounded art education that progresses logically, covers essential concepts and skills, aligns with educational standards, and fosters creativity and critical thinking. A well-developed curriculum guides the entire learning process.
Q8: What kind of art teacher training programs are available?
Programs range from undergraduate Bachelor’s degrees in Art Education to graduate Master’s and Doctoral programs. Many universities also offer post-baccalaureate certification programs for those who already hold a bachelor’s degree in a related field. Specialized workshops and professional development courses are also widely available.
By following these steps and committing to continuous growth, you can successfully embark on a rewarding career as an art teacher, inspiring the next generation of creators and thinkers.
