To become an art therapist in Georgia, you generally need a master’s degree in art therapy or a related field, followed by supervised clinical experience and passing a certification exam. What are the specific steps to achieve this? This comprehensive guide will walk you through the entire process, from education to licensure.
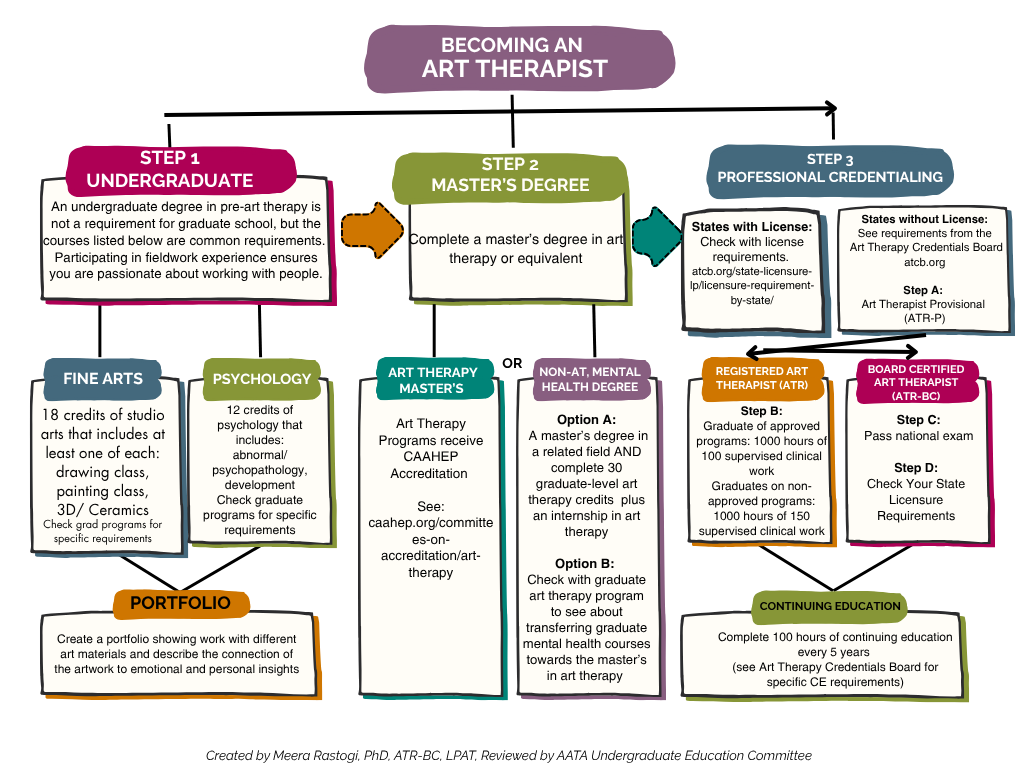
Image Source: arttherapy.org
Introduction to Art Therapy in Georgia
Art therapy is a powerful mental health profession that uses the creative process of art-making to improve the physical, mental, and emotional well-being of individuals of all ages. In Georgia, aspiring art therapists are guided by specific regulations and pathways to ensure they are well-prepared to serve their clients ethically and effectively. This guide delves into the essential steps for becoming a licensed art therapist Georgia, covering education, experience, and the crucial Georgia art therapy licensing requirements.
Georgia has a growing demand for mental health professionals, and art therapy offers a unique and vital approach to healing and self-expression. Whether you’re drawn to working with children, adults, or specific populations, pursuing art therapy in Georgia can be a deeply rewarding career. This guide aims to demystify the journey, providing clarity on the educational paths, practical experiences, and professional standards you’ll encounter.
The Foundation: Art Therapy Education Georgia
The cornerstone of becoming an art therapist is obtaining a quality education. In Georgia, this typically means pursuing a master’s degree.
Master’s Degree Programs in Georgia
When considering art therapy programs Georgia, it’s important to choose a program accredited by the American Art Therapy Association (AATA) or a program that meets the AATA’s educational standards. While Georgia may not have numerous programs solely dedicated to art therapy, several universities offer strong programs that align with these standards, often housed within counseling or psychology departments.
Here’s what to look for in a reputable art therapy education Georgia:
- Curriculum: The program should cover core art therapy principles, studio art, psychology, human development, counseling theories, ethics, and research methods.
- Faculty: Experienced and credentialed art therapists should be part of the faculty.
- Clinical Training: A strong emphasis on supervised practical experience is crucial.
- Accreditation: Ensure the program is accredited or meets the standards of the AATA.
While direct art therapy graduate programs Georgia might be limited, some institutions offer Master of Arts (MA) or Master of Fine Arts (MFA) degrees with an art therapy specialization or master’s degrees in counseling with an art therapy track. It’s essential to verify that the program’s coursework and internship placements will meet the requirements for Georgia art therapy licensing.
Essential Coursework
A typical master’s program preparing students for becoming a licensed art therapist Georgia will include courses such as:
- Foundations of Art Therapy
- Psychopathology
- Developmental Psychology
- Counseling Skills and Theories
- Art Therapy with Children
- Art Therapy with Adults
- Group Art Therapy
- Ethics in Art Therapy
- Research Methods in Art Therapy
- Studio Art Methods for Art Therapy
- Case Conceptualization and Treatment Planning
Choosing the Right Program
When researching art therapy programs Georgia, consider the following:
- Location: Proximity to your home or willingness to relocate.
- Program Focus: Does the program specialize in certain populations or therapeutic approaches?
- Faculty Expertise: Are the professors leaders in the field?
- Alumni Network: A strong network can be invaluable for career opportunities.
- Internship Opportunities: Investigate the quality and diversity of art therapy internships Georgia that the program facilitates.
The Practical Journey: Internships and Supervised Experience
Following your academic studies, gaining hands-on experience is paramount. This is where art therapy internships Georgia become vital.
The Role of Internships
Internships provide the practical application of theoretical knowledge learned in art therapy education Georgia. During an internship, you will work directly with clients under the guidance of a qualified supervisor. This experience is crucial for developing clinical skills, understanding different therapeutic settings, and fulfilling the requirements for becoming a licensed art therapist Georgia.
Key aspects of an art therapy internship:
- Client Interaction: Direct work with individuals, groups, or families using art-based interventions.
- Supervision: Regular sessions with a registered art therapist (ATR) or a board-certified art therapist (BCAT) to discuss cases, receive feedback, and refine techniques.
- Documentation: Learning to maintain accurate client records and progress notes.
- Professional Development: Engaging in case conferences, continuing education, and ethical decision-making.
Most accredited art therapy programs Georgia will incorporate a significant internship component as part of their curriculum. These internships are often structured to meet the supervised experience hours required for art therapy certification Georgia.
Post-Graduate Supervised Experience
After completing your master’s degree and internship, most pathways to becoming a licensed art therapist in Georgia will require additional supervised clinical experience. This period solidifies your skills and prepares you for independent practice. The specific number of hours and the qualifications of the supervisor are dictated by the licensing board.
The Georgia Board of Professional Counselors, Social Workers, and Marriage and Family Therapists is the primary body that oversees the licensing of mental health professionals in Georgia, including those who may practice art therapy. While Georgia doesn’t have a specific “Art Therapist” license category, individuals often seek licensure as Professional Counselors (LPC) with a specialization in art therapy, or they may hold the Registered Art Therapist (ATR) credential from the Art Therapy Credentials Board (ATCB) and practice art therapy under that designation, depending on the employment setting and specific state regulations.
Pursuing Professional Credentials and Licensing
To practice art therapy professionally and ethically in Georgia, obtaining appropriate credentials and licenses is essential.
Art Therapy Certification Georgia
The primary national credential for art therapists is the Registered Art Therapist (ATR) and the Registered Art Therapist-Provisional (ATR-P) offered by the Art Therapy Credentials Board (ATCB). To become an ATR, you must:
- Complete a master’s degree program that meets ATCB standards.
- Complete a supervised internship (usually 600 hours).
- Complete a specified period of post-graduate supervised clinical experience (typically 3,000 hours over at least 156 weeks).
- Pass the ATCB National Art Therapy Certification Examination.
Holding the ATR credential signifies a high level of competence and adherence to professional standards in the field of art therapy.
Georgia Art Therapy Licensing
In Georgia, the path to practicing as a licensed mental health professional often involves obtaining a Professional Counselor (LPC) license. While there isn’t a standalone “Licensed Art Therapist” license, individuals with art therapy backgrounds often pursue LPC licensure.
The Georgia Board of Professional Counselors, Social Workers, and Marriage and Family Therapists outlines the requirements for LPC licensure. These typically include:
- Master’s Degree: A master’s degree in counseling or a related field from an accredited institution. The degree must include a specific number of credit hours in counseling coursework. It is crucial that the art therapy education Georgia you receive meets these broader counseling degree requirements.
- Supervised Experience: A specific number of supervised clinical hours post-master’s degree. This often includes a minimum number of direct client contact hours and a certain number of supervision hours.
- Examination: Passing a national counseling examination, such as the National Counselor Examination for Licensure and Certification (NCE).
- Application and Fees: Submitting a complete application with all supporting documentation and paying the required fees.
It is vital for individuals interested in an art therapy career Georgia to ensure their master’s program and supervised experience align with the LPC licensure requirements in Georgia. Some art therapy graduate programs Georgia may offer tracks or coursework that specifically prepare students for LPC licensure.
The Interplay Between Certification and Licensure
It’s important to understand how art therapy certification Georgia (like the ATR) and state licensure (like LPC) work together.
- ATR Credential: Demonstrates your expertise specifically as an art therapist. Many employers, especially those focused on mental health and art therapy, will look for this credential.
- LPC License: Allows you to practice as a licensed professional counselor, which often includes the ability to provide psychotherapy and counseling services, including those incorporating art therapy. This license is often necessary for independent practice, insurance reimbursement, and working in certain clinical settings.
To have the broadest opportunities in an art therapy career Georgia, it is often beneficial to pursue both the ATR credential and an LPC license. This dual credentialing showcases both your specialized art therapy skills and your general competence as a licensed mental health professional.
Navigating the Requirements for Art Therapy Georgia
Successfully becoming a licensed art therapist Georgia involves carefully meeting all the established criteria.
Key Requirements Summary
Let’s consolidate the essential requirements for art therapy Georgia:
- Master’s Degree: Completion of a master’s degree from an accredited institution, with a curriculum that meets or exceeds the standards of the Art Therapy Credentials Board (ATCB) for those seeking ATR certification. If pursuing an LPC license, the degree must also meet the Georgia Board of Professional Counselors‘ requirements for counseling degrees.
- Supervised Internship: Successful completion of a supervised internship as part of the master’s program, typically involving direct client work and supervision by a qualified art therapist.
- Post-Graduate Supervised Experience: Accumulation of a specified number of post-graduate supervised clinical hours, working under the supervision of a licensed mental health professional. The exact number of hours and the supervisor’s qualifications will vary depending on whether you are pursuing ATR certification or an LPC license.
- National Examinations: Passing the ATCB National Art Therapy Certification Examination for ATR status, and typically the NCE for LPC licensure.
- State Application and Approval: Submitting a comprehensive application to the Georgia Board of Professional Counselors, Social Workers, and Marriage and Family Therapists, along with supporting documentation, and receiving approval for licensure.
Staying Updated on Regulations
It is crucial to regularly check the official website of the Georgia Board of Professional Counselors, Social Workers, and Marriage and Family Therapists for the most current and detailed Georgia art therapy licensing requirements. Regulations can change, and staying informed ensures your application process is smooth and successful.
The Art Therapy Career Georgia Landscape
An art therapy career Georgia offers diverse opportunities across various settings.
Where Art Therapists Work in Georgia
Art therapists find employment in a wide range of environments, including:
- Hospitals and Medical Centers: Working with patients dealing with chronic illness, trauma, or end-of-life issues.
- Mental Health Clinics and Community Centers: Providing therapy for individuals with various mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, PTSD, and eating disorders.
- Schools and Universities: Supporting students’ emotional and academic development, often through counseling services or specialized art therapy programs.
- Correctional Facilities: Helping incarcerated individuals process emotions, develop coping skills, and address behavioral issues.
- Rehabilitation Centers: Assisting individuals recovering from addiction, injury, or trauma.
- Private Practice: Establishing independent practices to offer art therapy services to a broad clientele.
- Non-profit Organizations: Working with specific populations, such as survivors of abuse, refugees, or individuals with disabilities.
Demand and Outlook
The demand for mental health services in Georgia continues to grow, and art therapists are increasingly recognized for their unique therapeutic contributions. As more people seek alternative and expressive forms of therapy, the art therapy career Georgia is projected to remain strong. Professionals who are well-credentialed, experienced, and possess strong clinical skills are likely to find ample employment opportunities.
Ethical Practice
Ethical practice is a cornerstone of all mental health professions. Art therapists in Georgia must adhere to the ethical codes set forth by the ATCB and any relevant state licensing boards. This includes maintaining client confidentiality, practicing within one’s scope of competence, fostering professional growth, and avoiding conflicts of interest.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the fastest way to become an art therapist in Georgia?
A1: The “fastest” way involves selecting an accredited master’s program that aligns with both ATCB requirements for ATR certification and Georgia’s LPC licensure requirements. Choosing a program with strong internship placements and diligently completing your post-graduate supervised hours without delay will also expedite the process.
Q2: Can I practice art therapy in Georgia with a master’s degree in art education and an art therapy certificate?
A2: While a master’s in art education with a certificate might provide foundational knowledge, it likely won’t meet the specific degree requirements for Georgia art therapy licensing as an LPC or for ATR certification by the ATCB. You typically need a master’s degree in art therapy or a closely related counseling field with a strong art therapy specialization from an accredited program. Always check the specific educational criteria set by the Georgia Board of Professional Counselors and the ATCB.
Q3: Who is responsible for art therapy licensing in Georgia?
A3: The Georgia Board of Professional Counselors, Social Workers, and Marriage and Family Therapists is responsible for the licensure of professional counselors, which is the primary route for licensed mental health practice that incorporates art therapy. The Art Therapy Credentials Board (ATCB) is responsible for national art therapy certification (ATR).
Q4: What are the key differences between ATR certification and LPC licensure in Georgia?
A4: ATR certification is a credential specifically for art therapists, demonstrating expertise in the field. LPC licensure is a state-issued license that allows you to practice as a professional counselor, which can include providing art therapy services, and is often required for independent practice and insurance reimbursement. Many art therapists in Georgia hold both.
Q5: How important are art therapy internships Georgia?
A5: Art therapy internships Georgia are critically important. They provide essential hands-on experience with clients, supervised practice to develop clinical skills, and are a mandatory component for both ATR certification and often for LPC licensure.
Q6: What if my art therapy graduate program Georgia is not explicitly accredited by the AATA?
A6: If your program is not AATA-accredited, you must verify with the ATCB and the Georgia Board of Professional Counselors that your specific degree and coursework meet their equivalency standards for becoming a licensed art therapist Georgia or an LPC. It’s crucial to get this clarification before enrolling.
Conclusion
Embarking on the path to becoming an art therapist in Georgia is a journey that requires dedication to education, hands-on experience, and adherence to professional standards. By carefully selecting an accredited master’s program, diligently completing your art therapy internships Georgia and post-graduate supervised hours, and understanding the Georgia art therapy licensing requirements, you can establish a fulfilling and impactful career. Whether you aim for ATR certification or LPC licensure, or both, this guide provides the foundational knowledge to navigate your way to a rewarding art therapy career Georgia. Remember to always consult the official resources of the Georgia Board of Professional Counselors and the ATCB for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
